How Does The Stock Market Work?
Have you ever wondered ‘How does the Stock Market work? Who enables these buy and sell orders? Investors pay a particular price to buy a share, but do you know how the stock price is determined? You probably already know about ‘Supply and Demand’, so how does it govern the price of a stock? You, with a few clicks on an app, can enjoy partial ownership of some of the world’s biggest companies. Let’s take a detailed look at how the stock market works and how and where exactly the stock is traded.
Related articles:
- How Does The Stock Market Work?
- Market Types: Primary and Secondary Markets
- Players Enabling Trades in Stock Market
- Stock Exchange
- The Stock Markets Across The Globe: World’s Biggest Stock Exchanges
- Stock Brokerage Firm or Stock Broker
- Investors
- Clearing Firm or Clearing House
- How does a Stock Trade Happen?
- How Does the Stock Market Work if There is No One Ready to Buy or Sell?
- How is The Stock Price Determined?
- How to View The Bid Ask Spread?
- Conclusion
Market Types: Primary and Secondary Markets
Primary Market
Primary Market is where investors can buy the stocks (and bonds) directly from the company when first offered (mostly during an IPO or Initial Public Offering). The buyers in the primary market are mostly large institutional investors.
Smaller investors, or retail investors, with a few thousand dollars to invest rarely get to buy desirable stocks in the primary market.
Secondary Market
Retail investors (common investors) can buy and sell the shares of the company’s stock once they start trading on the stock market, which essentially is the Secondary Market. Simply put, if you buy shares on New York Stock Exchange, Nasdaq, Tokyo Stock Exchange or other similar exchanges, you’re buying shares on the secondary market.
5 Players Enabling Trades in Stock Market
Here is a list of the 5 prominent entities that enable stock trades in the stock market.
- Stock Exchange
- Stock Brokerage Firm
- Investors
- Clearing Firm
- Market Makers
We will briefly cover what roles they play in the stock market trades below.

Stock Exchange
A stock exchange, like any exchange or a marketplace, has two sides – the buy-side and a sell-side. It is an online or physical place where investors can buy and sell stocks. Trading on the stock exchange is regulated and there are guardrails in place to prevent stock price manipulation and investor abuse.
Nasdaq is a popular Online Stock Exchange. There are many Physical Stock Exchanges across the world, for example, New York Stock Exchange, London Stock Exchange, Tokyo Stock Exchange, etc.
You can find the stock exchange information easily on your brokerage app or simply on Google Finance.
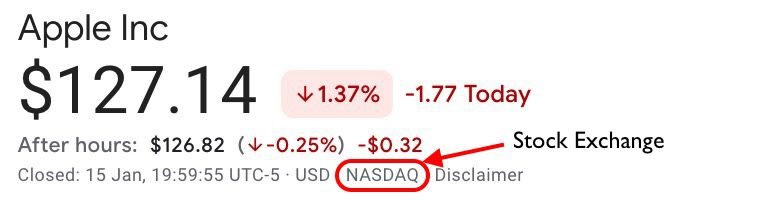
The Apple stock on Nasdaq Stock Exchange.
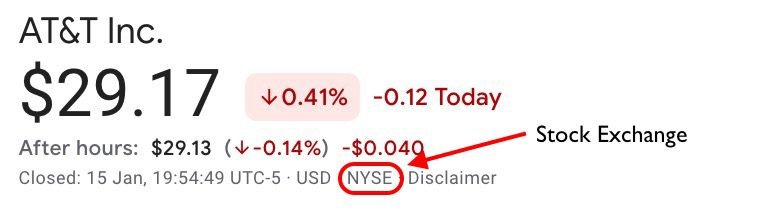
AT&T Stock on New York Stock Exchange.
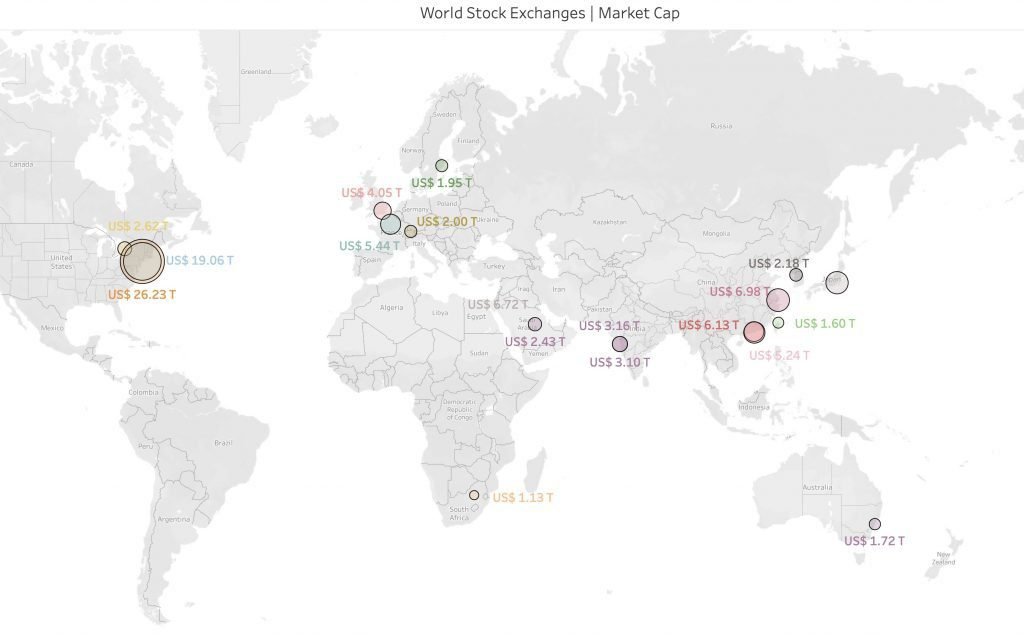
The Stock Markets Across The Globe: World’s Biggest Stock Exchanges
Here is the list of the biggest stock exchanges in the world, by market cap.
| Exchange | Country | Market Cap (US$Trillion) | Short Name | City |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| New York Stock Exchange | United States | 26.232 | XNYS | New York City |
| Nasdaq | United States | 19.06 | XNAS | New York City |
| Shanghai Stock Exchange | China | 6.975 | XSHG | Shanghai |
| Japan Exchange Group | Japan | 6.718 | XJPX | Tokyo |
| Hong Kong Stock Exchange | Hong Kong | 6.13 | XHKG | Hong Kong |
| Euronext | France | 5.443 | XPAR | Paris |
| Shenzhen Stock Exchange | China | 5.238 | XSHE | Shenzhen |
| London Stock Exchange | United Kingdom | 4.045 | XLON | London |
| Bombay Stock Exchange | India | 3.16 | XBOM | Mumbai |
| National Stock Exchange | India | 3.1 | XNSE | Mumbai |
| Toronto Stock Exchange | Canada | 2.62 | XTSE | Toronto |
| Tadawul | Saudi Arabia | 2.43 | XSAU | Riyadh |
| Deutsche Borse | Germany | 2.284 | XFRA | Frankfurt |
| Korea Exchange | South Korea | 2.176 | XKOS | Seoul |
| Nasdaq Nordic Exchanges | Sweden | 1.95 | Stockholm | |
| SIX Swiss Exchange | Switzerland | 2.001 | XSWX | Zurich |
| Australian Securities Exchange | Australia | 1.72 | XASX | Sydney |
| Taiwan Stock Exchange | Taiwan | 1.598 | XTAI | Taipei |
| JSE | South Africa | 1.13 | XJSE | Johannesburg |
Stock Brokerage Firm or Stock Broker
Once you have decided to invest in stocks, you need to set up a mechanism to place buy and sell orders on the stock exchange(s). It is not easy for retail investors (aka common people) to open a direct trading account at the stock exchange. You need someone to help you place buy and sell orders on the exchange. Brokerage firms help you do that.
Brokerage firms, or Broker-Dealers, are FINRA regulated financial institutions that act as the middle man enabling the buy and sell trades on stock exchanges. Investors can open an account with a brokerage firm and place trade orders online, via telephone, in-person depending on the service model of the firm. Brokerage firms also tend to charge a fee or commission for every trade order (buy or sell) they execute for you. The charges can quickly add up for someone making frequent trades and can eat up a chunk of profits for small investors. Some brokers don’t charge the investors any fees for the buy and sell orders, hence might be a better fit for smaller investors.
Depending on the broker, an investor may be able to purchase stocks listed on international exchanges. For example, a person living in Barcelona can buy stocks trading on Nasdaq and invest in his favorite companies. That’s global investing for you!
Full Service Brokers
Full-Service Brokers provide an array of features and services such as executing stock buy and sell orders, wealth management, retirement account, trade via telephone, etc. to investors. They typically charge commissions and fees on services. Full-Service Brokers may be a great fit for some people.
Full-Service Brokers may charge a fixed commission per trade (say, $7.95 per trade). Beginner investors aiming to place simple buy and sell trades might not find the fees worth it.
Discount Brokers
We generally associate Discount Brokers with fewer service offerings, such as basic stock trading, online-only trading, etc. They charge low or no commissions for executing trades. They are perfect for beginner investors who want to invest small to medium amounts in the stock market.
The discount brokers, however, in today’s world are adding more and more features to close the gap with traditional full-service brokers. For example, M1 Finance also offers IRA (Individual Retirement Account) to investors.
Related article: Best Investment App
Investors
A critical component of the stock market is the investors themselves. Investors are categorized into two broad categories: retail investors and institutional investors.
Investors, both retail and institutional, can place buy and sell orders.
Institutional Investors
Institutional investors are generally organizations that trade a large volume of securities such as stocks, bonds, derivatives (such as stock options). Due to the sheer volume of trades they can execute, institutional investors get access to primary markets (i.e. they can buy a company’s stock shares even before its IPO). They also qualify for preferential rates on commissions on trades etc.
An asset management firm such as Ray Dalio’s Bridgewater Associates is an institutional investor.
Retail Investors
Retail investors are the common people who invest in the stock market. They generally don’t have access to the primary market and can only buy and sell shares on the secondary market (the stock market). Retail investors invest in stocks via brokerage accounts or retirement accounts such as 401(k).
Clearing Firm or Clearing House
With a few clicks, an investor can buy or sell shares. However, to ensure the money gets to the seller’s account and the shares get to the buyer’s account, we need a Clearing Firm. Clearing Firms handle behind-the-scenes operations to actually execute and record the trade transactions.
In some cases, the brokerage firm doubles up as the clearing firm as well, while in some cases they may be different entities.
How does a Stock Trade Happen?
Buy Command and Sell Command
Buyer searches for the stock he or she wants to buy, configures a stock order type (market order, limit order, etc.), enters the price and quantity, and hits the ‘buy’ button.
Similarly, a Seller configures a sell order and hits the ‘sell’ button.
Order Relay
The ‘Buy’ order is captured by the brokerage firm and relayed on to the Stock Exchange.
Similarly, the ‘Sell’ order is captured and relayed to the Stock Exchange.
Order Matching
The buy-side orders are arranged in descending order, and the highest price order gets priority in execution. The sell-side orders are arranged in ascending order, and the lowest price order gets priority in execution. Generally, a FIFO (First In First Out method) is used to determine which buy order is executed first in case of multiple buy orders at the same price point. Similarly, FIFO is used on the sell-side as well.
Effectively, a ‘buy’ order is matched against a ‘sell’ order i.e. buying and selling orders are brought together to see if the desired quantity is available at the desired price. As orders match, they start getting executed.
All of this process happens fairly quickly are there are algorithms in place to ensure the rules are followed during stock trade execution.
Order Execution or Order Fill
The order can get fully or partially executed or stay unexecuted for a while, depending on the demand and supply dynamics (or bid and ask prices). We will discuss the bid and ask spread in detail below.
How Does the Stock Market Work if There is No One Ready to Buy or Sell?
We believe the above process was easy to understand. Buyer places an order, seller places an order, orders are matched and everyone gets home happy.
But you might be wondering, are there always sellers placing orders to match against buy orders? If not, what happens then?
This is where the Market Makers come into play.
Market Makers
Market Makers are firms that actively buy and sell stocks listed on stock exchanges at the current quoted share prices. They do so to maintain liquidity in the market. So, for the popular stocks, even if there is no individual available for selling you a stock, most likely the market makers would be willing to do the trade with you (in hopes of getting a better trade for themselves).
Market Maker carries the risk of buying a stock and being unable to sell it later at a better price. You would notice that not all stocks have high liquidity, simply because the market makers don’t want to take on the additional risk for trading those stocks.
How is The Stock Price Determined?
In primary markets, the stock price is straightforward and upfront, as decided by the underwriters. The investors can buy the shares directly from the issuing company.
In the secondary market or stock exchanges, the stock price is dynamic and changes every second. So, how does the stock price go up or down? Let’s break it down.
Bid Price
Buyers can place ‘bids’ or their desired buying price and quantities they would like to purchase at that price point.
Ask Price
Sellers can place ‘asks’ or their desired selling price and quantities they would like to sell at that price point.
Bid-Ask Spread
the difference between the bid price and ask price is called the bid-ask spread. investors are advised to trade stocks that have a narrow bid-ask spread, it is an indication that the stock has good tradeability.???
Stock Price
Technically, the Stock Price is the price at which the stock was last traded.
A good estimation of the stock price is the mid-point of the bid-ask price, in the case of narrow spreads. For example, let’s say the highest bid is $99 per share, and the lowest ask is $99.10 per share. In this case, the bid-ask spread if $0.10, and the mid-point of the bid-ask price is $99.05.
$99.05 would be a good estimate of the stock price.
How to View The Bid Ask Spread?
Level 1 data shows the highest bid and lowest ask price.
In the Webull screenshot attached, the highest bid at the moment is $208.38 and the lowest ask is $208.61
The bid-ask spread is $208.61 – $208.38 = $0.23 or 23 cents.

Level 1 data shows the highest bid and lowest ask price.
In the Webull screenshot attached, the highest bid at the moment is $208.38 and the lowest ask is $208.61
The bid-ask spread is $208.61 – $208.38 = $0.23 or 23 cents.
Level 2 data gives a better idea of market depth on both the buy and sell sides.
Level 2 data shows multiple highest bids and multiple lowest ask prices.
In the Webull screenshot attached, the highest bid at the moment is $207.74 and the lowest ask is $207.76
The bid-ask spread is $207.76 – $207.74 = $0.02 or 2 cents.
Looking at the market depth, an investor can gauge the demand and supply in a better manner.
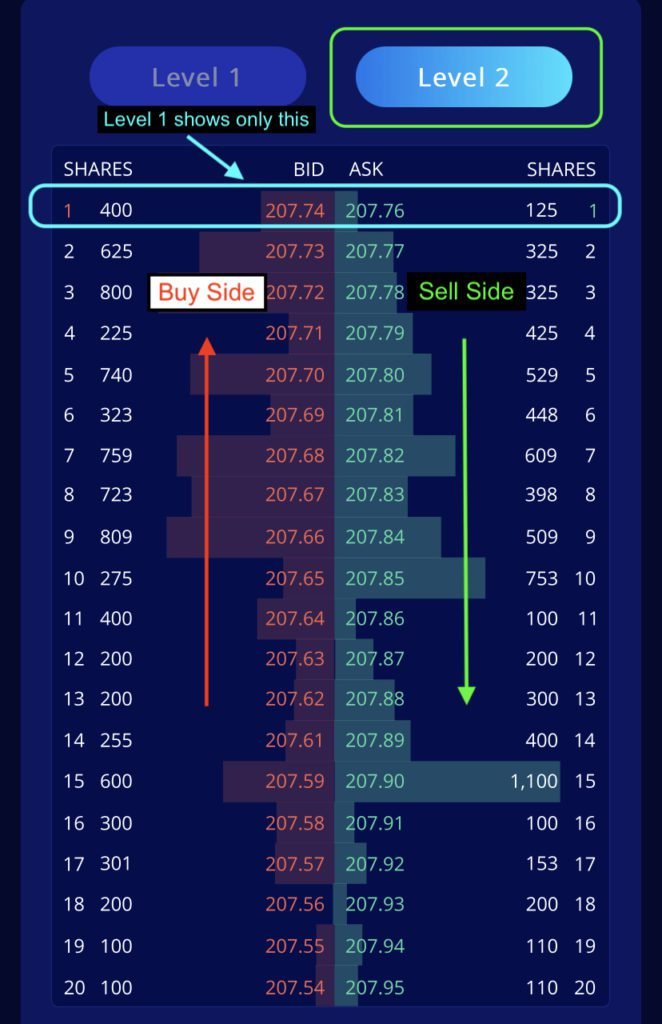
Level 2 data shows multiple bids and multiple ask prices.
In the Webull screenshot attached, the highest bid at the moment is $207.74 and the lowest ask is $207.76
The bid-ask spread is $207.76 – $207.74 = $0.02 or 2 cents.
Looking at the market depth, an investor can gauge the demand and supply in a better manner. For example, if an investor wants to sell 2000 shares of the stock, he has the following demand:
- 400 shares at $207.74
- 625 shares at $207.73
- 800 shares at $207.72
- 225 shares at $207.71
- remaining 450 shares can be sold at $207.70
If he places a ‘market sell’ order, he knows what price he should expect to get for his sale of 2500 shares.
Conclusion: How The Stock Market Works
You can place orders easily to buy and sell shares on the stock market. There is a lot of entities working behind the scene to make your trades happen. We hope this article was informative and enhanced your understanding of how the stock market works.
We’d love your feedback if you want to share.

Read more
Popular Topics: Stocks, ETFs, Mutual Funds, Bitcoins, Alternative Investing, Dividends, Stock Options, Credit Cards
Posts by Category: Cash Flow | Credit Cards | Debt Management | General | Invest | Mini Blogs | Insurance & Risk Mgmt | Stock Market Today | Stock Options Trading | Technology
Useful Tools
Student Loan Payoff Calculator | Mortgage Payoff Calculator | CAGR Calculator | Reverse CAGR Calculator | NPV Calculator | IRR Calculator | SIP Calculator | Future Value of Annuity Calculator
Home | Blog

Page Contents